3D layer
1. 3D layers overview and resources
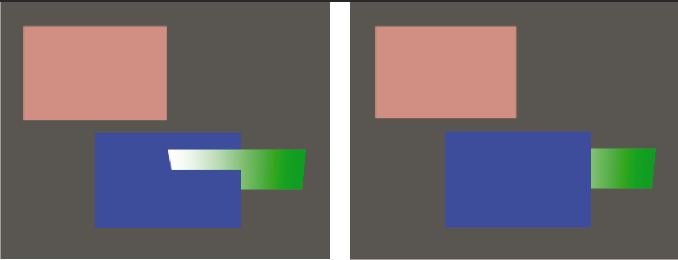
When you make a layer a 3D layer, the layer itself remains flat, but it gains additional properties: Position (z), Anchor Point (z), Scale (z), Orientation, X Rotation, Y Rotation, Z Rotation, and Material Options properties. Material Options properties specify how the layer interacts with light and shadows. Only 3D layers interact with shadows, lights, and cameras.

2D layers (left) and layers with 3D properties (right)
By default, layers are at a depth (z-axis position) of 0. In the software, the origin of the coordinate system is at the upper-left corner; x (width) increases from left to right, y (height) increases from top to bottom, and z (depth) increases from near to far.
You can transform a 3D layer relative to the coordinate space of the composition, the coordinate space of the layer, or a custom space by selecting an axis mode.
You can add effects to 3D layers, composite 3D layers with 2D layers, and create and animate camera and light layers to view or illuminate 3D layers from any angle. When rendering for final output, 3D layers are rendered from the perspective of the active camera. (See Create a camera layer and change camera settings.)
All effects are 2D, including effects that simulate 3D distortions. For example, viewing a layer with the Bulge effect from the side does not show a protrusion.
2. Convert 3D layers
When you convert a layer to 3D, a depth (z) value is added to its Position, Anchor Point, and Scale properties, and the layer gains Orientation, Y Rotation, X Rotation, and Material Options properties. The single Rotation property is renamed Z Rotation.
When you convert a 3D layer back to 2D, the Y Rotation, X Rotation, Orientation, and Material Options properties are removed, including all values, keyframes, and expressions. (These values can be restored by converting the layer back to a 3D layer.) The Anchor Point, Position, and Scale properties remain, along with their keyframes and expressions, but their z values are hidden and ignored.
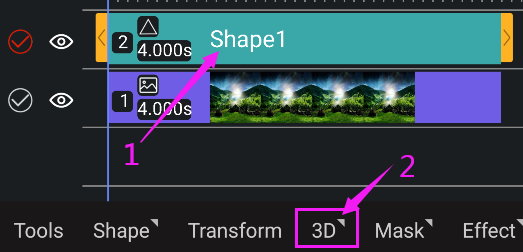
Convert a layer to a 3D layer
Select the layer and click 3D. Click to turn on the 3D switch.
Convert a 3D layer to a 2D layer
Select the layer, then click 3D, and click to turn off the 3D switch.
3. Rotate or orient a 3D layer
You can rotate a 3D layer by changing its Rotate value. In this case, the layer rotates its anchor point.
When you animate any of the X Rotation, Y Rotation, or Z Rotation attributes, the layer rotates along each axis based on each attribute value. That is, the Rotation value specifies the angular alignment. Animating the Rotate property allows the layer to rotate multiple times, providing more precise control.
To rotate a 3D layer, select the layer to rotate, click Transform, and click the pencil icon next to the name of the rotation attribute.
The first part of the Rotation attribute value is the number of full rotations; the second part is the degree of partial rotations.

3. 3D layer interaction
A 3D layer does not affect any layers on the other side of the 2D layer in the 2D layer or layer stack order. Similarly, a 3D layer does not intersect with any layers on the other side of the 2D layer in the 2D layer or layer stack order.